Hemangioma
Hemangioma is a congenital lesion that may be observed in the liver.
This vascular lesion is benign and, in most cases, it has been accidentally discovered and dose not need any treatment.
In cases where this lesion causes symptoms such as pain or bleeding, it will need care and treatment.

Hemangiomas treatment
In the past, the only treatment method for hemangioma was surgery, which cannot be performed in most cases. Today, using semi-invasive endo-vascular therapies, the vessels supplying blood to hemangioma can be blocked. Thereby, hemangioma will be inactive in the form of a dead tissue and finally becomes very small.
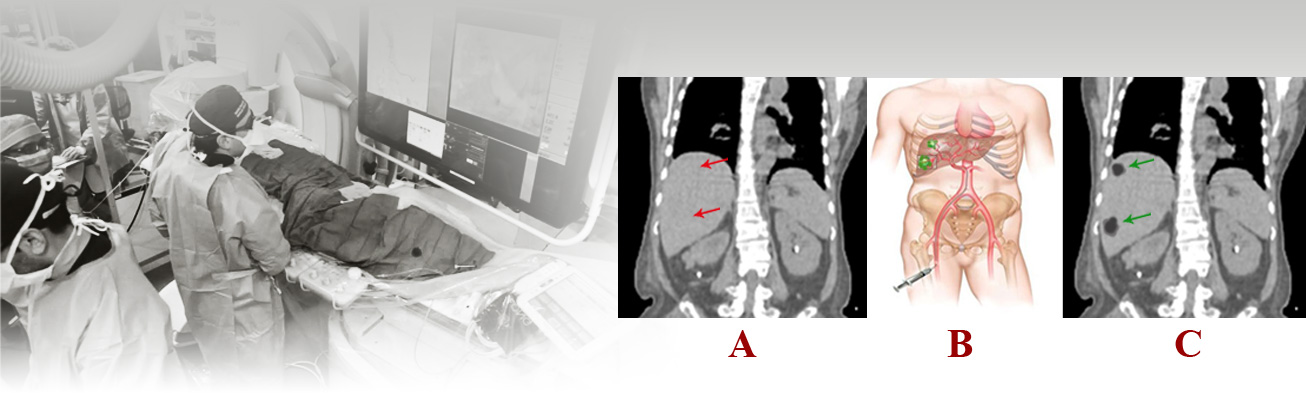
Liver embolization procedure
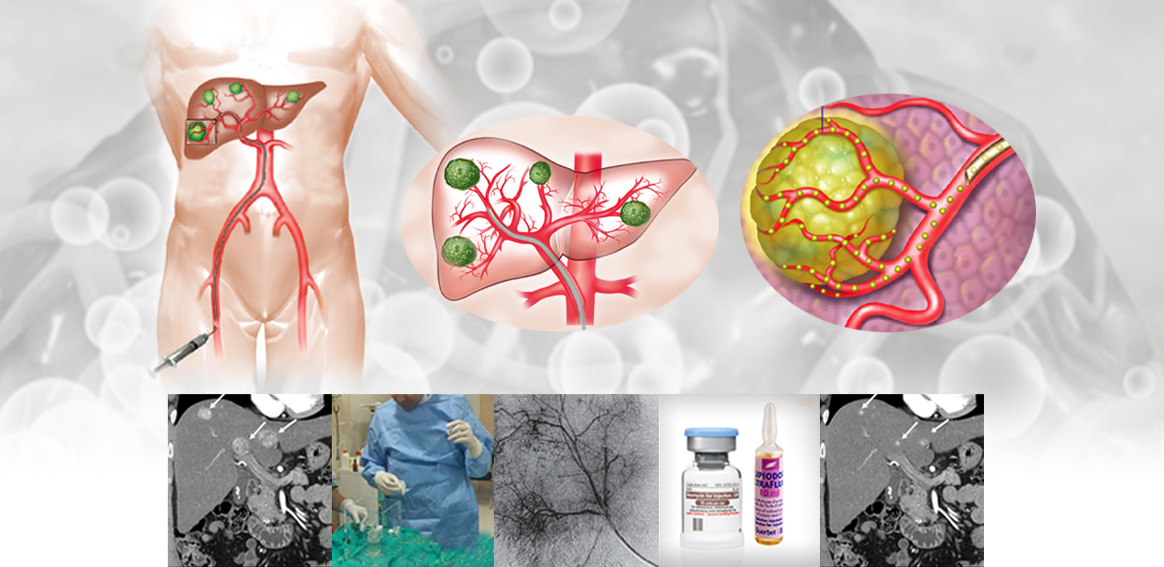
Once the radiologist observes the medical records and confirms hemangioma tumor under the guidance of imaging devices, a catheter will be inserted into the liver artery (at the beginning of the arteries supplying blood to hemangioma) through the right groin under local anesthesia.
After the injection of a contrast agent and determination of the location of hemangioma, combined blockers will be injected into the hemangioma artery and the surgery process will always be checked through imaging.
After the injection of blockers, the catheter will be removed and, to avoid bleeding, the incision will be closed with Angio-Seal or with firm manual pressure.
After bandage is applied to the incision, sandbags will be placed on it for 1 to 2 hours to prevent bleeding.
The right groin should be immobile for at least 24 hours and, if necessary, the cut should be compressed manually.
Hepatic hemangioma embolization will be performed without incision and only with a cut of few millimeters in the groin. After a short time, there will be no trace of the cut and it has significant advantages to surgery.
The advantages of embolization:
It is performed without anesthesia and it has much fewer complications than surgery
The patient will return to normal life as soon as possible
It causes the least bleeding compared to surgery
Recurrence precentage is very low.