


Nuclear medicine
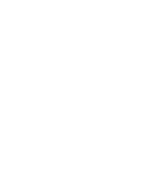
Nuclear medicine is the science of diagnosis and treatment of diseases with radioactive substances. Radiopharmaceuticals are similar to the molecules within the body and are traceable from the outside of the body. So, after administration of radiopharmaceuticals, different organs of the body and changes caused by diseases can be easily examined and many diseases can be diagnosed, tracked and the response to the treatment can be assessed even before they are detected by anatomical imaging methods such as CT scans. The Nuclear Medicine Department of Pardise Noor
Medical Imaging Center, with advanced, state-of-the-art equipment, is capable of doing many high quality scans. Some of the services provided in this section and their applications include :

Contribution to tumor staging
Detection of tumor recurrence
Assessment of tumor response to the treatment
Differentiation of viable tumor tissue from necrotic/fibrotic tissue
Contribution to the determination of the nature of some tumors (benign/malignant/neuroendocrine)
Including the examination of bone metastasis and assessment of tumors including cancer of breast, prostate, lung, neuroendocrine tumors, and lymphoma, tumors of the brain and soft tissue and bone is performed using radiopharmaceuticals such as:
Tc-MDP
Gallium, thallium
Tc-MIB,
DMSA
Alkaline octreotide
Discovering and scanning Sentinel node in breast cancer and melanoma for diagnosing lymphatic metastasis
Differentiation of hemangioma from liver metastasis
Treatment of painful bone metastases
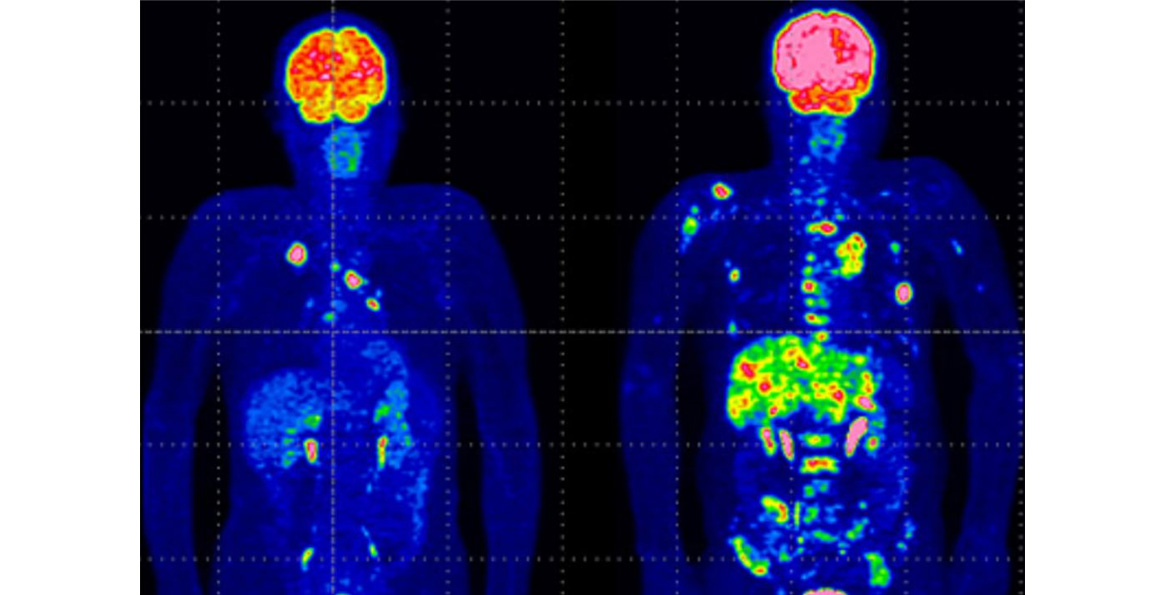
Osteomyelitis
Underlying stress fractures
Bone metastases
Examination of bone pain with no known cause
Examination of TMG for detecting the cause of pain or jaw deviation
SPECT (Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography) for evaluation of lesions in complex bones such as spine, wrists, and osteoid osteoma
Medical radiosynovectomy for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and hemophilic arthritis
Avascular necrosis
Prosthetic complications including infection
Polyarthritis
Examination of the number of bone lesions
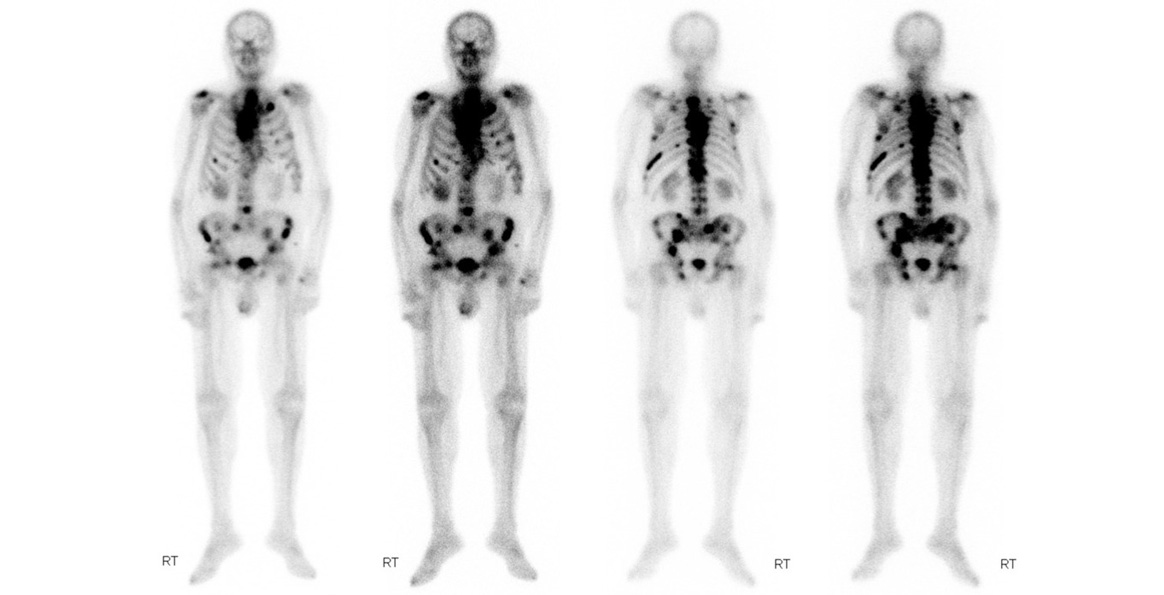
Evaluation of renal function with
Direction: Tc-DTPA
Differentiation of hydronephrosis from obstructive uropathy and review of neonatal hydronephrosis
Diagnosis of renovascular hypertension
Evaluation of complications of implanted kidney
Evaluation of kidneys in case of contrast allergy
GFR
Evaluation of renal parenchyma
For diagnosis: Tc-DMSA
Acute pyelonephritis (APN) and the resulting scars
Congenital renal disorders
Pseudotumors
Renal trauma
Determination of the separate function of kidneys
Scrotal scan: for distinguishing torsion from epididymitis
Radioisotopic cystography: for detecting reflux and following up treatment
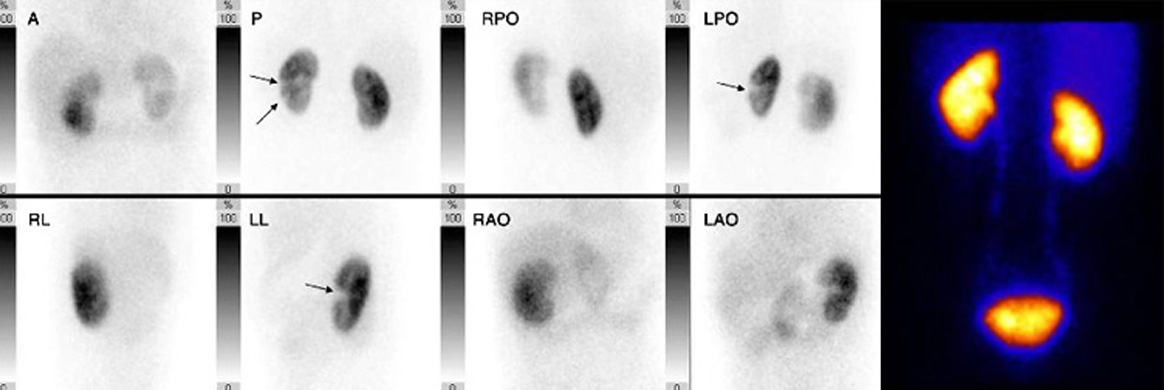
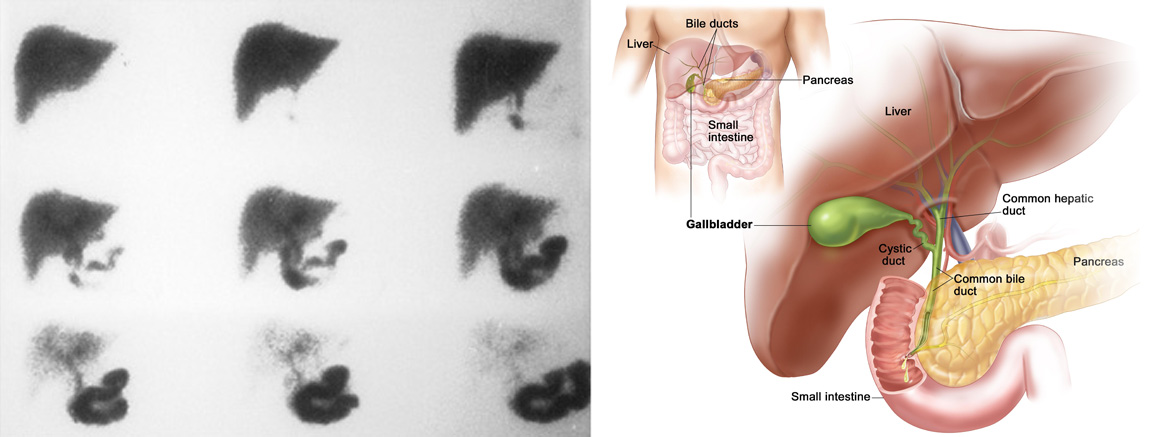
Scan of the bile ducts
Acute cholecystitis
Biliary atresia
Chronic biliary diseases
Complications after biliary surgeries
Liver and spleen scan
Parenchymal liver diseases such as cirrhosis and hepatitis
Liver tumors, focal nodular hyperplasia
Budd-Chiari syndrome
Accessory spleen and Splenosis
Supplemental diverticular scan: for examining ectopic gastric mucosa
Hepatic hemangioma scan: for differentiating hemangioma from other liver tumors
Gastrointestinal bleeding scan: for diagnosing lower gastrointestinal bleeding and estimating its approximate location
Gastrointestinal tract function
Diagnosis of esophageal reflux and evaluation of the response to treatment
Esophageal transit
Emptying of the stomach
Intra-arterial treatment and imaging of liver tumors
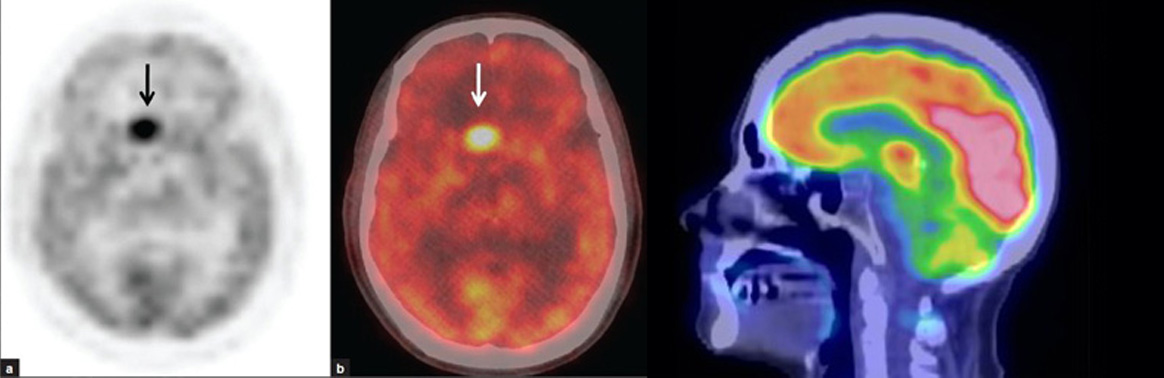
Brain perfusion SPECT imaging with
Dementia including Alzheimer’s and MCI
Cerebrovascular disorders such as
TIA
Neurological complications including brain post-trauma
Convulsion
Brain scan with technetium
Examination of brain death
Herpetic encephalitis
Radioisotopic Systrnography and brain shunt scan
Examination of CSF leak
Investigation of shunt patency
Diagnosis of hydrocephalus
NPH and communicating
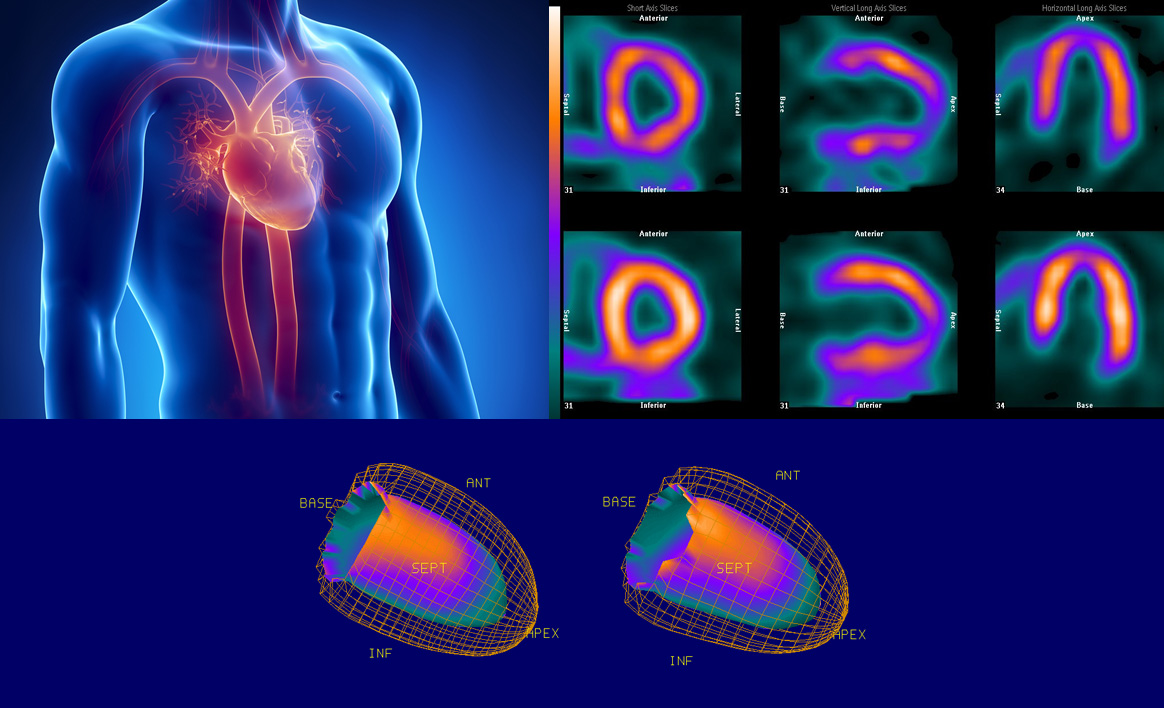
Diagnosis of coronary artery disease (CAD)
Determination of prognosis in patients with
(CAD)
Assessment of the response to therapy
Assessment of the patients before surgery
Assessment of viable myocardial tissue
In all mentioned cases, it is possible to assess myocardial perfusion, and to perform Gated imaging for determining EF, wall motions and heart function.
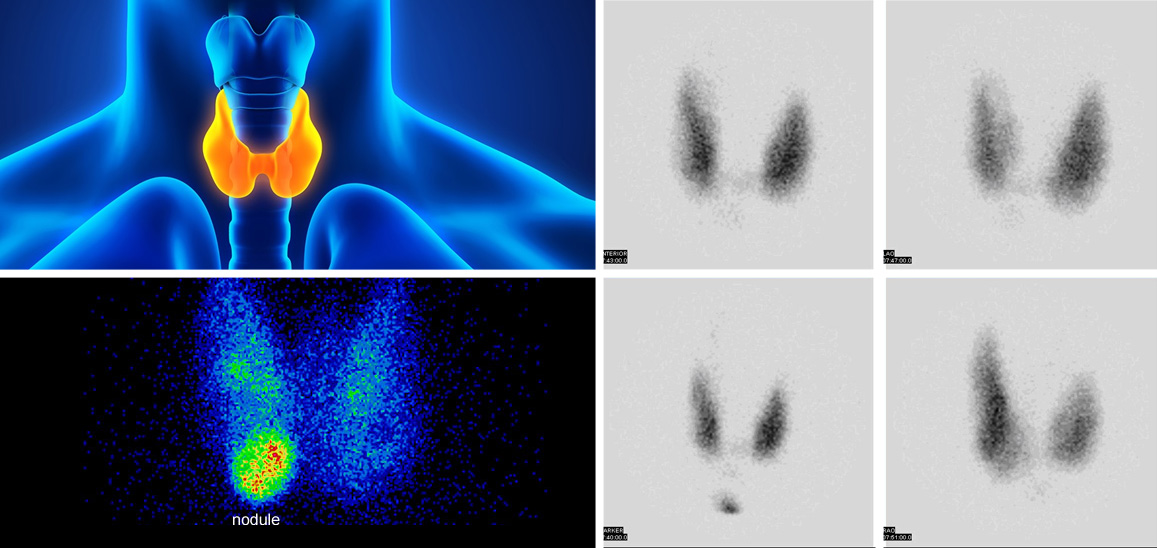
Thyroid scan for the evaluation of thyroid nodules, differentiation of thyroiditis from hyperthyroidism, neonatal hyperthyroidism, and ectopic thyroid
Parathyroid scan with SPECT for detecting parathyroid adenoma
Detection of neuroendocrine tumor and review of its metastases
Treatment of hyperthyroidism
Scan of tear ducts for detecting the possible location of tear duct obstruction
Lung perfusion scan for diagnosis and follow-up of pulmonary embolism, detection of left to right shunt, determination of separate function of lungs before lung surgery
Examination of infection especially in prosthesis, with gallium scan and
Tc-UBI
The diagnosis of sarcoidosis and its activity with gallium scan
It should be noted that:
In the Nuclear Medical Center of Pardise Noor, patients who are unable to cooperate, including children, may be scanned using anesthesia.