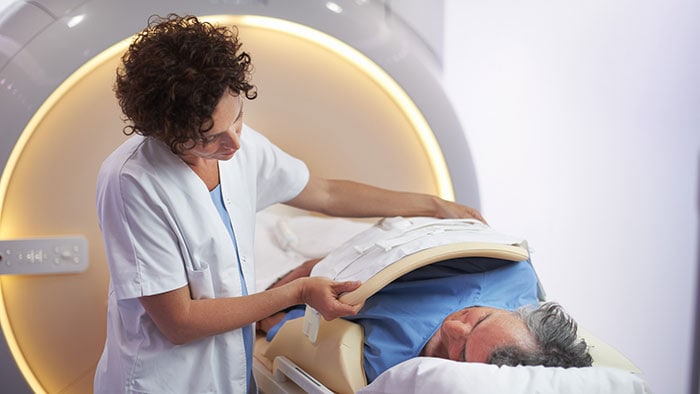
MRI or Magnetic resonance imaging is one of the advanced medical imaging methods. Using this method, the images of bodies internal tissues can be seen and thereby, the problems and diseases of the body members can be detected.
X-ray is not used in MRI. Waves used in MRI are radio and magnetic waves that are not harmful to the body.
MRI is a precise, powerful imaging technique for diagnosing problems and disease of body tissues. MRI and CT are different in that the former provides clear, precise images of soft tissues such as cartilage, tendons, ligaments, nerves, and blood vessels and this imaging method is especially useful for diagnosing the disease of these tissue.
The MRI imaging method is used more to assess the problems in soft tissue, while CT scan is more useful to examine bones and their lesions and damages.
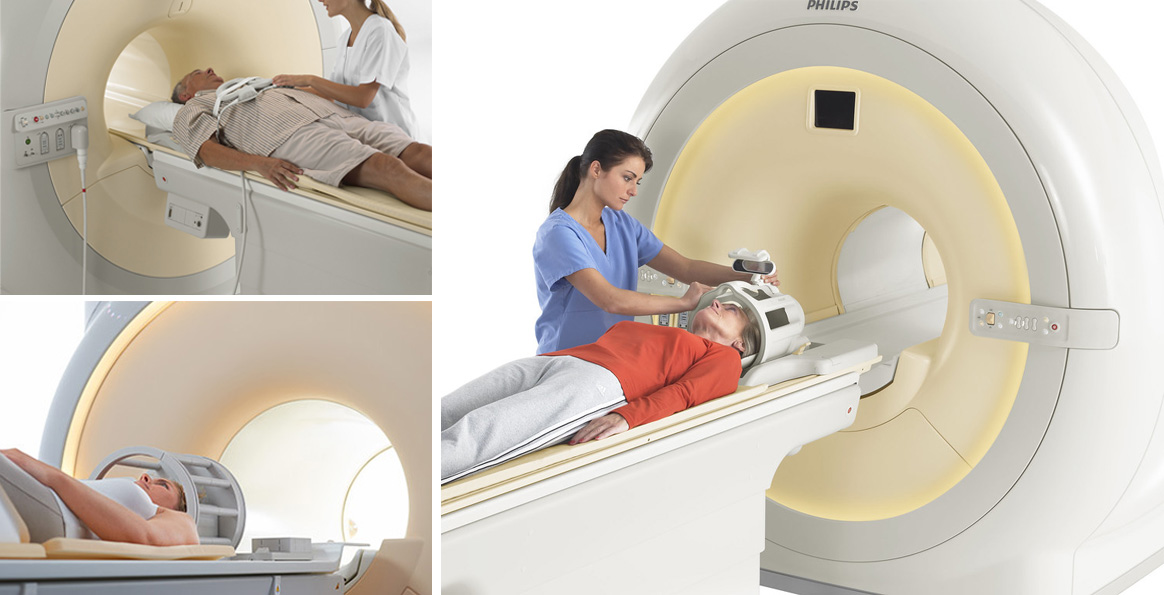
MRI is a low-risk imaging method. Annually about 10 million people undergo MRI. MRI is completely painless with no known short-term or long-term complications.
A mentioned, MRI uses a very powerful magnetic field.
Metal objects start moving in the presence of a magnetic field. The movement of these objects may cause damage to the patient. Thus, there must be no metal object in the MRI room. If the patient has a metal object with him/her, he/ she must leave it outside the MRI room.
Watches, accessories, and some parts of clothes are metallic.
If the patient has already undergone a surgery in which metal clamps had been used on his/her vessels, MRI is dangerous for him/her because metal clamps can move in the magnetic field of MRI. Metal bullets or shrapnel in he patients body can also cause the same problem. In the patients who use a hearing aid or heart pacemaker, MRI magnetic waves can interfere with the operation of this device.
Available Services
-MRI of the brain, orbit and optic nerve, olfactory nerve
-MRI of ear for cochlear implants
-MRI ESF flow study
-MRI of offal body through contrast material injection
-MRI under anesthesia
-MR Angiography (MRA) of cerebrovascular and carotid arteries, upper limb, lung, abdomen, pelvis, and lower limb, MR angiography of renal artery
-MRV, venography of cerebrovascular and carotid arteries, upper limb, thorax, abdomen, pelvis, and lower limb
-MR Mammography (MRM) and MRI axillary areas
-MRI of placenta and fetus
-Dynamic MRI of pitutiary and liver
-MRI of the heart, mediastinum, and liver
-MRI of the heart and liver to assess iron load
-MR arthrography of all joints
-MRI of joints and limbs, MRI of sacroiliac joint, separate and integrated MRI of spinal cord, and TMG
-MRCP
-MRI of the abdomen and pelvis for examining the organs
-MRI of the abdomen and pelvis for tumor staging
-MR fistolography and examination of pelvic abscess
-MRV and examination of the kidneys and bladder and urinary tract
-MRI of pelvis for examining the rectal tumor





