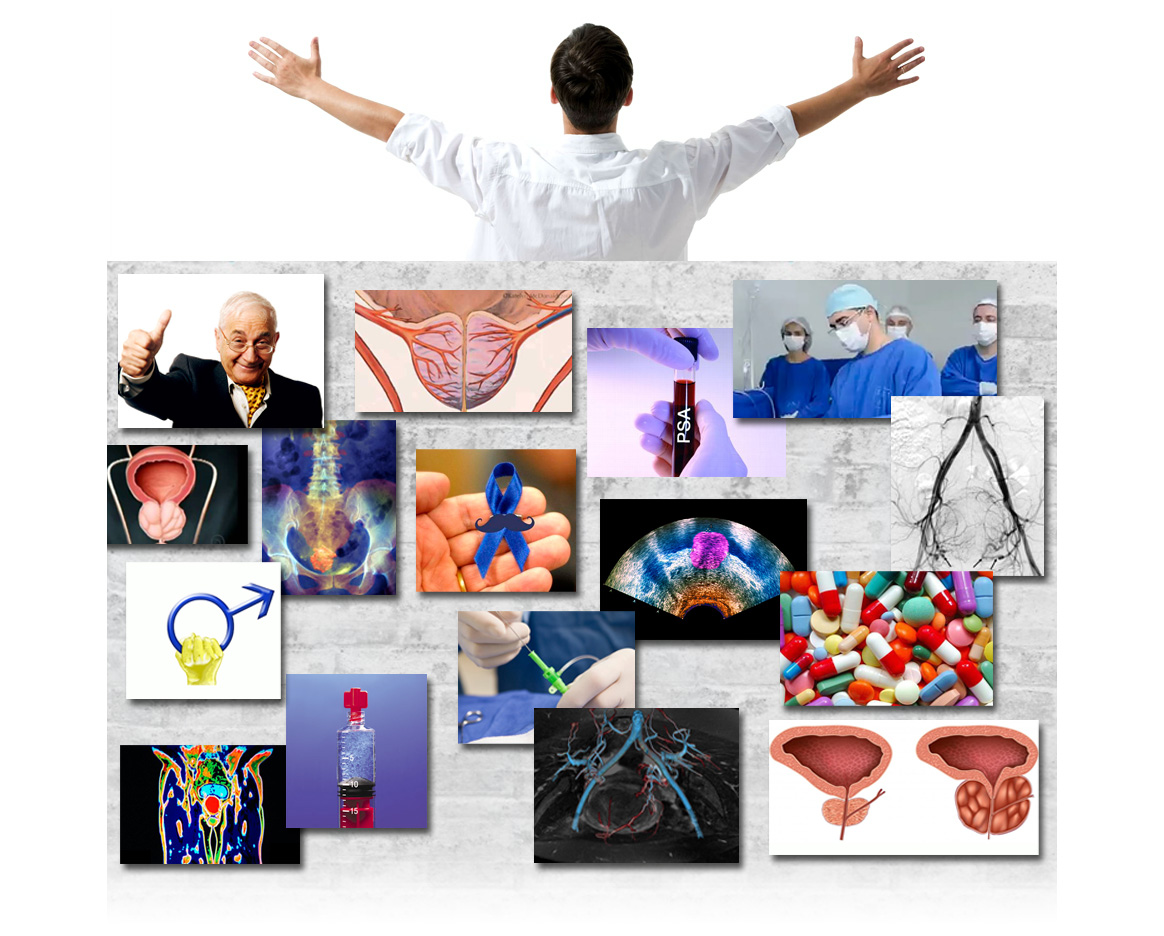
The prostate is a small gland located below the bladder that surrounds the urethra opening. This urethra carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body.
Prostate Function :
It includes bladder control, keeping sperms, and fertility in men.
Symptoms of Prostate Disease :
Frequent urination, dysuria, difficulty starting urination etc.
Prostate disease:
Inflamation of Prostatitis
Prostatitis is the inflammation of the prostate (small gland below the bladder). This inflammation can be acute (acute prostatitis) or chronic or recurrent (chronic prostatitis), whichi is caused by a bacterial infection and usually associated with bladder and urinary tract infections.
Acute prostatitis is usually caused by the dispersion of urinary tract infection or sexually transmitted diseases.
Dysuria along with severe deep pain between the legs are among the symptoms of prostatitis.
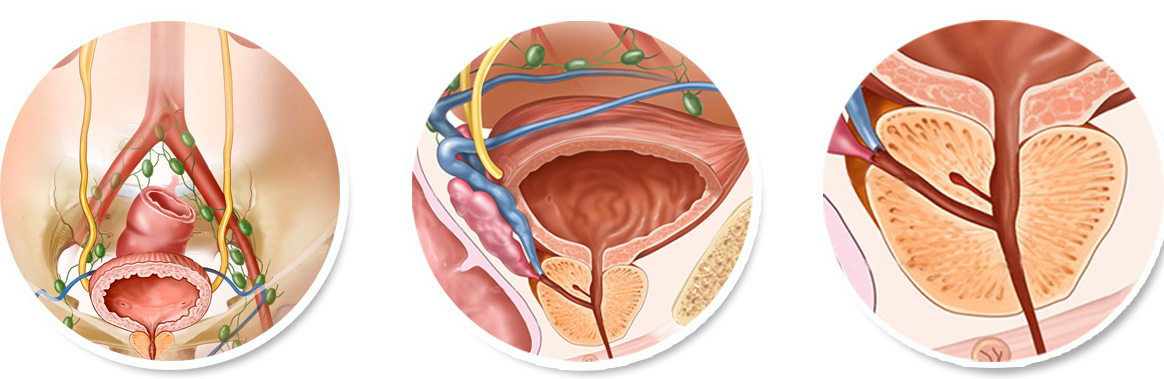
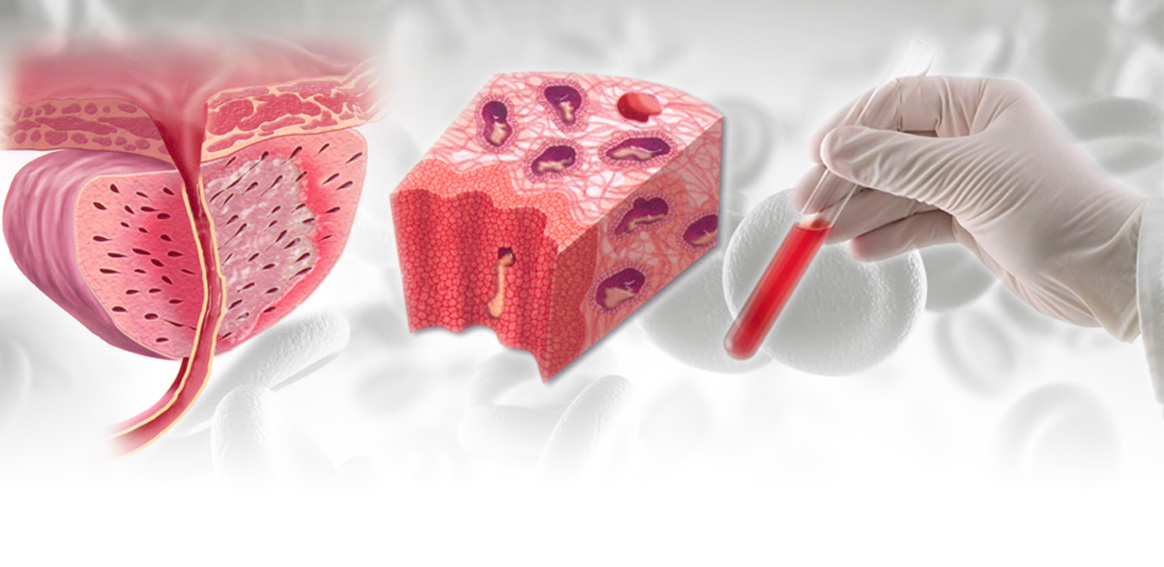
Prostate Cancer
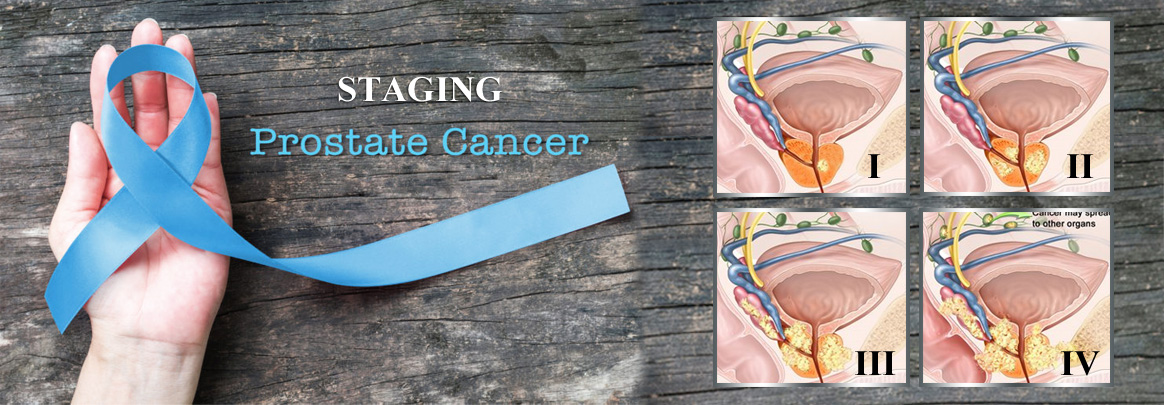
Prostate cancer is a common disease in men. However, it rarely develops in patients below 50 but develops more in older men.
Prostate cancer usually progresses slowly and is initially limited to the prostate gland and will not be usually dispersed to other parts of the body.
If prostate cancer is diagnosed early, there will be an excellent chance for successful treatment.
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
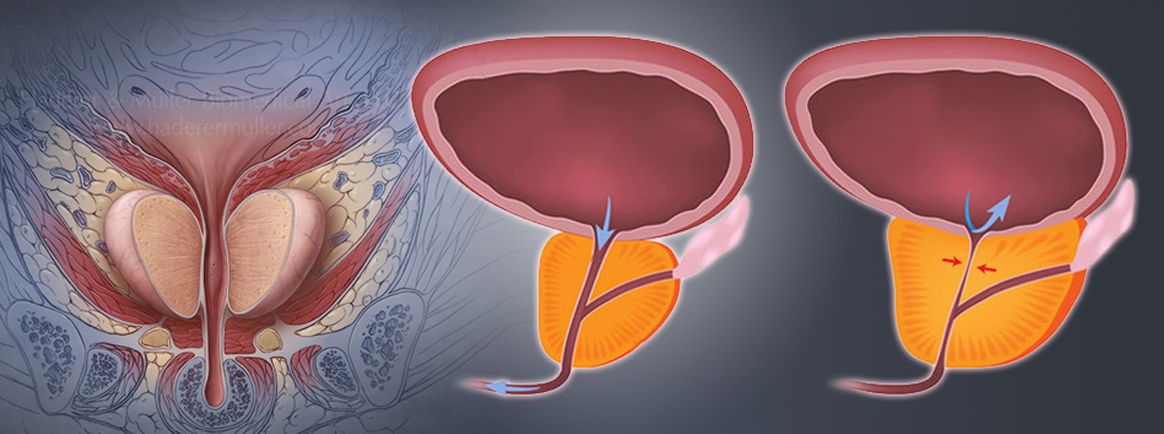
Prostatic hyperplasia
The prostate is a walnut-sized gland in young men. With aging, the gland increases in size. Benign enlargement of the prostate is called BPH (benign prostatic hyperplasia).
This process can cause problem such as frequent urination, urinary tract infection or complete obstruction of the urinary tract.
Treatment of BPH or benign prostatic hyperplasia
The most common treatment method for BPH is to use medication and surgery, but recently the minimally invasion procedure of prostate artery embolization has been recommended for treating this disease. It is a very good option for patients who do not meet the conditions for general anesthesia or cannot be operated. That is because it can be performed as an outpatient procedure without hospitalization.
Prostatic artery embolization
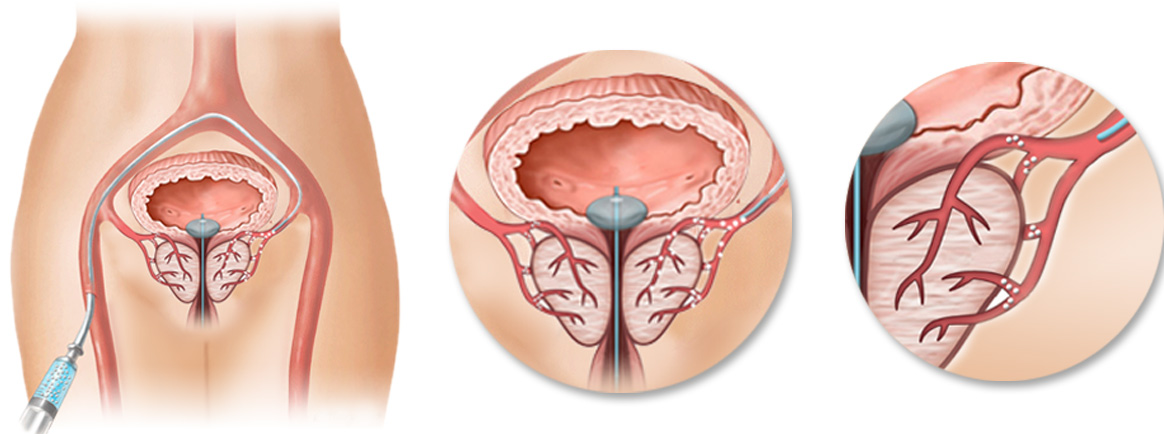
Prostate artery embolization can be performed under the guidance of imaging devices with local anesthesia. That is, a catheter will be inserted into prostatic artery through the right groin artery. After angiography of the intended place, combined blockers will be injected into the prostatic artery.
By performing this surgery, the artery supplying blood to the prostate will be blocked and the prostate will shrink. This surgery does not require anesthesia and can be performed as an outpatient procedure.
Preparations for surgery:
– Fasting for approximately 6 hours before the surgery
– Having the patients medial records
– having blood coagulation test results
-Taking shower and removing unwanted hair from the groin
– Having a companion to do the paperwork
– Stopping medications such as Aspirin, Warfarin, or Plavix, 3 days before the surgery