


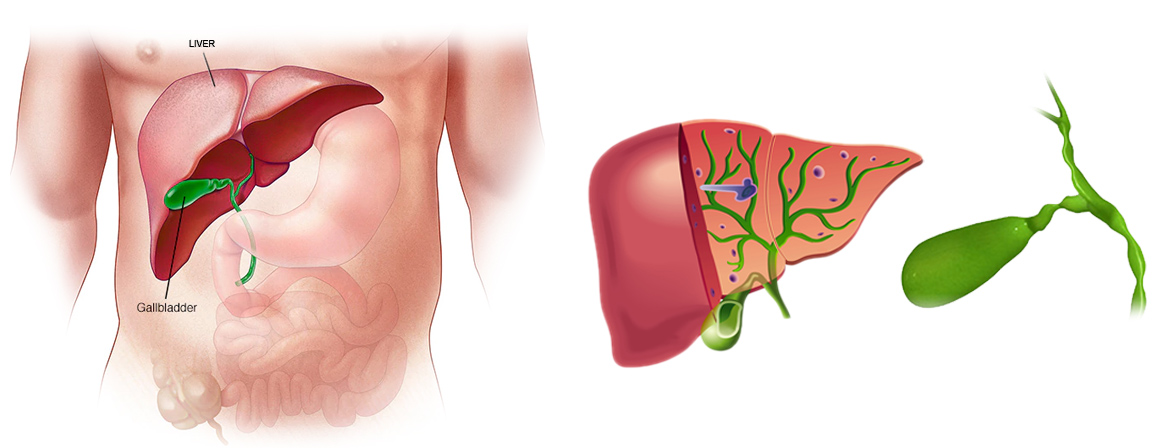
Bile function
The function of bile is to help digest foods, especially fatty material. When food enters from the stomach into the intestine, bile will be flushed through the duct into the intestine.
If the patient bile duct function is impaired due to cancer, an autoimmune disease, of adhesion it will cause stenosis or obstruction of bile ducts, with regard to which special measures need to be taken.
Obstruction of bile ducts causes increased bilirubin in the blood, jaundice, skin rashes, and a total lack of life quality.
In this condition, by seeing a specialist in order to remove the symptoms (jaundice and obstructions), you may be recognized as a candidate for surgery, ERCP, or PTC.
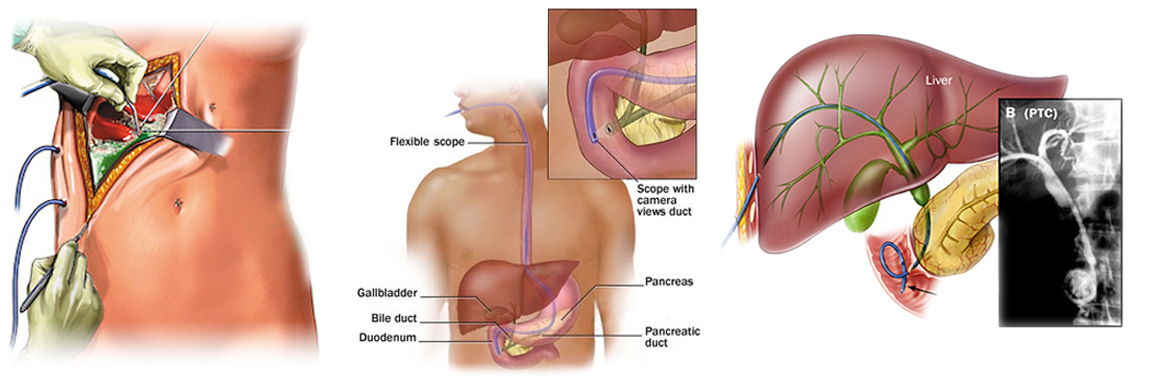 SURGERY ERCP PTC
SURGERY ERCP PTC
Starting this treatment requires accurate, complete imaging such as ultrasound, endosonography, MRCP, CT scan, and even biopsy in some cases.
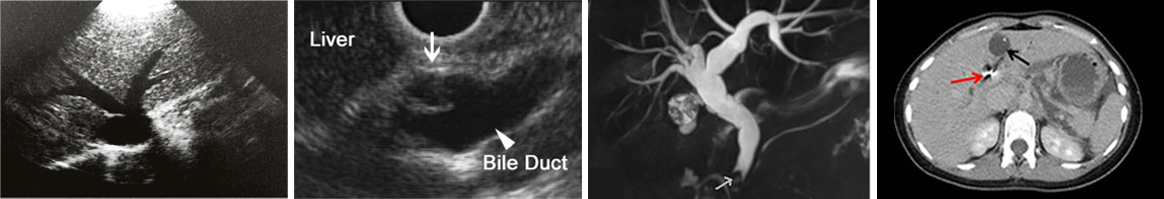
SONOGRAPHY ENDOSONOGRAPHY MRCP CT SCAN
– Ultrasound and CT scan and MRCP imaging can be performed at this clinic.
– Endosonography imaging can be performed in gastroenterology clinics.
PTC
When ERCP or surgery is unsuccessful, the patient will be a candidate for PTC per-cutaneous drainage.
This surgery will be performed via the 3 following methods:
– Internal metal stents
– External biliary drainage
– Internal/ecternal biliary drainage
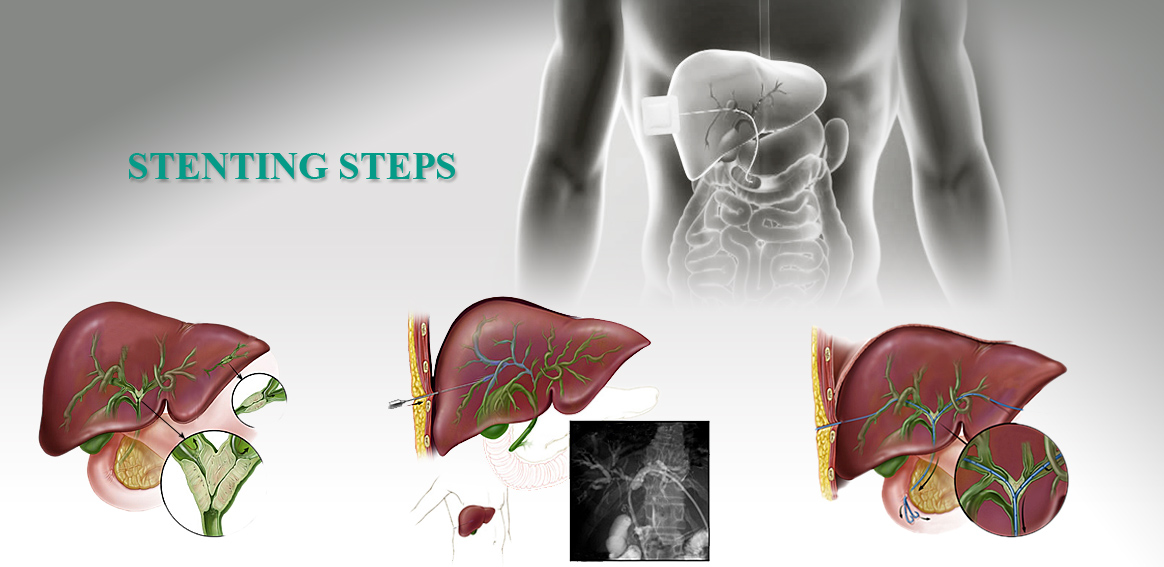
BILIYARY METAL STENTING
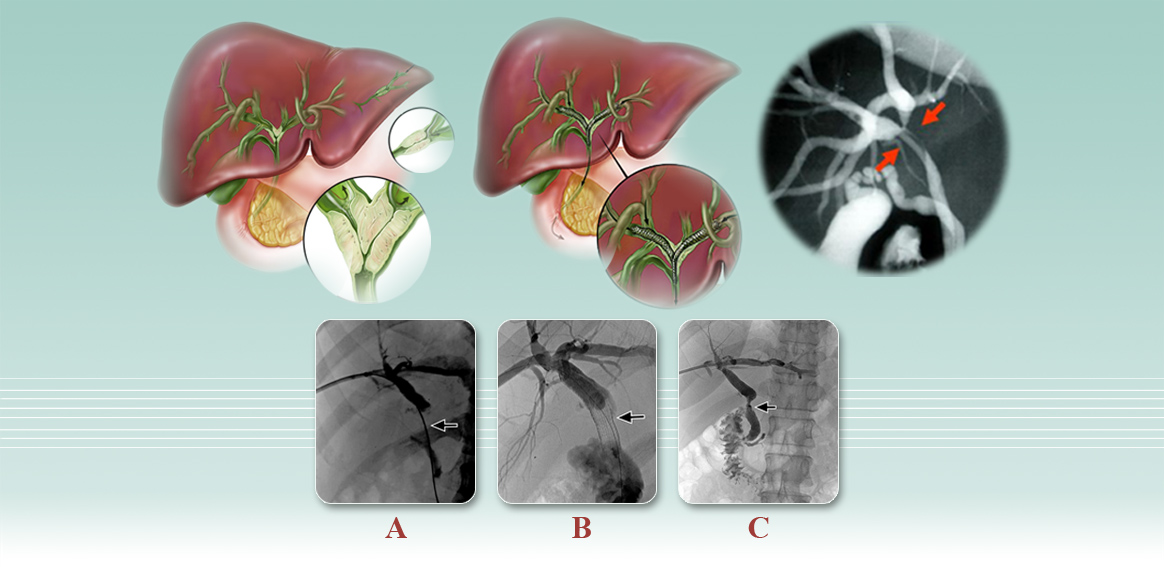
The patient attends the clinic with symptoms of bile duct obstruction and high bilitubin and he/she will be recognized as a candidate for this procedure after evaluating the medial records of imaging, blood coagulation tests, and obstruction position.
Appropriate stent and balloon will be considered according to the length of stenosis. In most cases, anesthesia is not required. However, dilatation of bile duct that causes severe pain requires anesthesia.
Thus, under the guidance of ultrasound and fluroscopy (CRM), dilated ducts in the liver will be selected and, then, punctured by an 18-gauge needle. After passing the springs (guidewire) through the stenosis, the stenosis will be opened by angioplasty balloon and stenting will be performed.
The patient will be examined for hematoma and bile leakage and eventually all tools will be removed and there will be nothing but an incision of a few millimeters o the surface of the skin.
Internal/external plastic stent
Metal stents are placed completely inside the duct, but plastic stents are like catheter (hose), the beginning of which that has a number of holes will be placed in the intestine.
The middle part of the catheter or stent including a number of holes will be placed inside the biliary duct and stenosis and the end of the catheter or stent, which is outside the skin and connected to the faucet, will be fixed to the skin by suture and fixator.
In cases where the preparation of metal stent is not affordable, this method is a good option.
The method is just like metal stent except that the stent type is different.
After the operation, the patient will be evaluated for hematoma and bile leakage and a maker will be put on the catheter for preventing the catheter from moving and enabling bile drainage into the intestine. In this type pf stent, bag will not be attached to the catheter. The catheter connects to the bag only when necessary and approved by the doctor, for a certain period of time.
This type of stent should be replaced every 3 to 4 months and after the obstruction is unblocked, it should be completely exit from the body.
It is not hard to keep this catheter, just you should be careful about catheter displacement.
External plastic stent
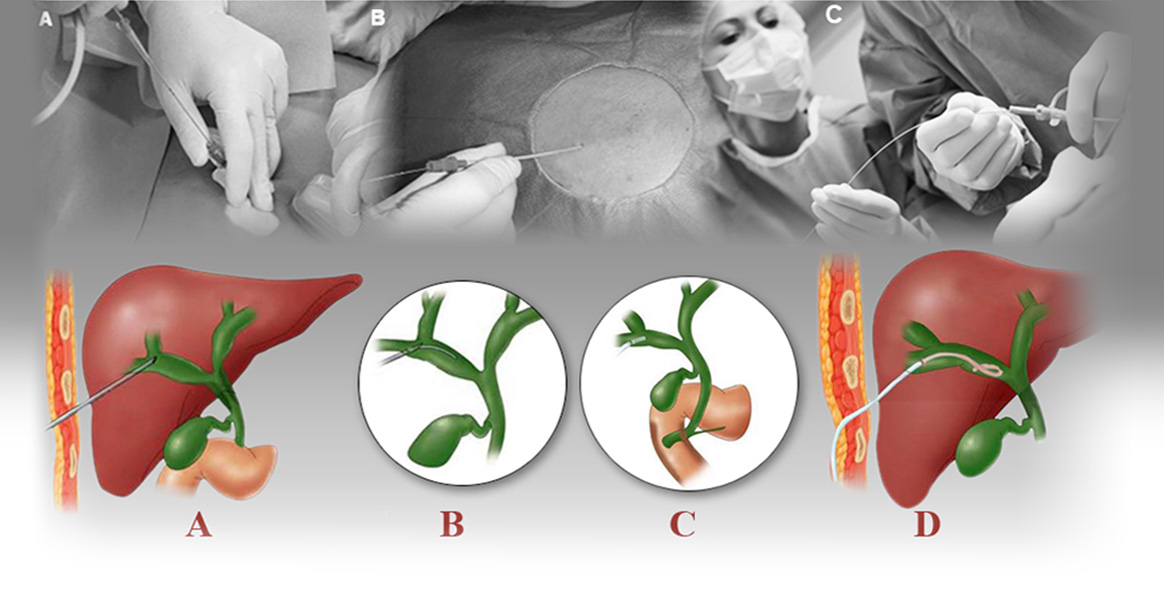
When it is impossible to pass through bile ducts stenosis, the doctor will insert the external plastic stent.
That is, under the guidance of ultrasound and fluroscopy (CRM), first, dilated ducts in the liver will be selected and, then, punctured by an 18-gauge needle. After passing (guidewire) springs through the stenosis, the stenosis will be dilated by plastic tubes with appropriate sizes (dilator) and, then, the external plastic stent will be placed in the bile duct. Accordingly, bile drainage will be established with the difference that bile will exit from the body, and the bag will become connected to the end of the plastic stent, which is out of the skin. It is a little difficult to keep the bag because the hose (bag connector) is long and hard to control.
Most patients complain of stents external maintenace because it is fixed to the skin only with a few stiches and a fixator and it will come off from the intended spot with the smallest stretch and bile drainage will not be performed.
Bile duct dilatation